Inflammatory bowel disease
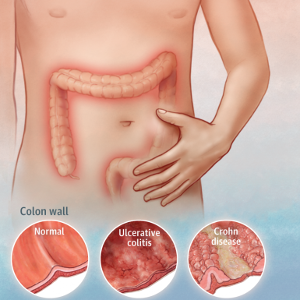
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of chronic inflammatory conditions of the intestine, with Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the main types. The incidence of IBD has rapidly increased in recent decades, with an estimated 5 million people living with IBD globally. IBD is a relapsing-remitting disorder and all currently available treatments aim at reducing the symptoms of acute inflammation to keep the patient in a remission state. However, treatments often offer only limited relief and patients may develop resistance over time. Given the complexity and heterogenicity of the disease, there is an urgent need for biomarkers and personalized therapies targeting novel mechanisms of action.



